MenuModel
Added in version 2.32.
Superclasses: Object
Subclasses: DBusMenuModel, Menu
GMenuModel represents the contents of a menu — an ordered list of
menu items. The items are associated with actions, which can be
activated through them. Items can be grouped in sections, and may
have submenus associated with them. Both items and sections usually
have some representation data, such as labels or icons. The type of
the associated action (ie whether it is stateful, and what kind of
state it has) can influence the representation of the item.
The conceptual model of menus in GMenuModel is hierarchical:
sections and submenus are again represented by GMenuModel’s.
Menus themselves do not define their own roles. Rather, the role
of a particular GMenuModel is defined by the item that references
it (or, in the case of the ‘root’ menu, is defined by the context
in which it is used).
As an example, consider the visible portions of this menu:
An example menu
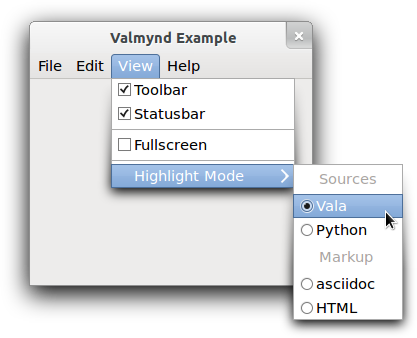
There are 8 ‘menus’ visible in the screenshot: one menubar, two submenus and 5 sections:
the toplevel menubar (containing 4 items)
the View submenu (containing 3 sections)
the first section of the View submenu (containing 2 items)
the second section of the View submenu (containing 1 item)
the final section of the View submenu (containing 1 item)
the Highlight Mode submenu (containing 2 sections)
the Sources section (containing 2 items)
the Markup section (containing 2 items)
The example <``a`-menu-example>`_ illustrates the conceptual connection between
these 8 menus. Each large block in the figure represents a menu and the
smaller blocks within the large block represent items in that menu. Some
items contain references to other menus.
A menu example
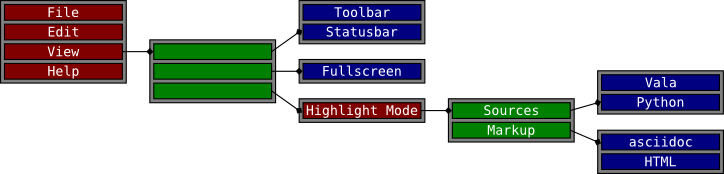
Notice that the separators visible in the example <``an`-example-menu>`_
appear nowhere in the menu model <``a`-menu-example>`_. This is because
separators are not explicitly represented in the menu model. Instead,
a separator is inserted between any two non-empty sections of a menu.
Section items can have labels just like any other item. In that case,
a display system may show a section header instead of a separator.
The motivation for this abstract model of application controls is
that modern user interfaces tend to make these controls available
outside the application. Examples include global menus, jumplists,
dash boards, etc. To support such uses, it is necessary to ‘export’
information about actions and their representation in menus, which
is exactly what the action group exporter and the menu model exporter do for
ActionGroup and MenuModel. The client-side
counterparts to make use of the exported information are
DBusActionGroup and DBusMenuModel.
The API of GMenuModel is very generic, with iterators for the
attributes and links of an item, see
iterate_item_attributes and
iterate_item_links. The ‘standard’ attributes and
link types have predefined names: G_MENU_ATTRIBUTE_LABEL,
G_MENU_ATTRIBUTE_ACTION, G_MENU_ATTRIBUTE_TARGET, G_MENU_LINK_SECTION
and G_MENU_LINK_SUBMENU.
Items in a GMenuModel represent active controls if they refer to
an action that can get activated when the user interacts with the
menu item. The reference to the action is encoded by the string ID
in the G_MENU_ATTRIBUTE_ACTION attribute. An action ID uniquely
identifies an action in an action group. Which action group(s) provide
actions depends on the context in which the menu model is used.
E.g. when the model is exported as the application menu of a
`GtkApplication <https://docs.gtk.org/gtk4/class.Application.html>`_,
actions can be application-wide or window-specific (and thus come from
two different action groups). By convention, the application-wide actions
have names that start with app., while the names of window-specific
actions start with win..
While a wide variety of stateful actions is possible, the following is the minimum that is expected to be supported by all users of exported menu information:
an action with no parameter type and no state
an action with no parameter type and boolean state
an action with string parameter type and string state
Stateless
A stateless action typically corresponds to an ordinary menu item.
Selecting such a menu item will activate the action (with no parameter).
Boolean State
An action with a boolean state will most typically be used with a ‘toggle’ or ‘switch’ menu item. The state can be set directly, but activating the action (with no parameter) results in the state being toggled.
Selecting a toggle menu item will activate the action. The menu item should be rendered as ‘checked’ when the state is true.
String Parameter and State
Actions with string parameters and state will most typically be used to represent an enumerated choice over the items available for a group of radio menu items. Activating the action with a string parameter is equivalent to setting that parameter as the state.
Radio menu items, in addition to being associated with the action, will have a target value. Selecting that menu item will result in activation of the action with the target value as the parameter. The menu item should be rendered as ‘selected’ when the state of the action is equal to the target value of the menu item.
Methods
- class MenuModel
- get_item_attribute_value(item_index: int, attribute: str, expected_type: VariantType | None = None) → Variant | None
Queries the item at position
item_indexinmodelfor the attribute specified byattribute.If
expected_typeis non-Nonethen it specifies the expected type of the attribute. If it isNonethen any type will be accepted.If the attribute exists and matches
expected_type(or if the expected type is unspecified) then the value is returned.If the attribute does not exist, or does not match the expected type then
Noneis returned.Added in version 2.32.
- Parameters:
item_index – the index of the item
attribute – the attribute to query
expected_type – the expected type of the attribute, or
None
- get_item_link(item_index: int, link: str) → MenuModel | None
Queries the item at position
item_indexinmodelfor the link specified bylink.If the link exists, the linked
MenuModelis returned. If the link does not exist,Noneis returned.Added in version 2.32.
- Parameters:
item_index – the index of the item
link – the link to query
- is_mutable() → bool
Queries if
modelis mutable.An immutable
MenuModelwill never emit theMenuModel::items-changed signal. Consumers of the model may make optimisations accordingly.Added in version 2.32.
- items_changed(position: int, removed: int, added: int) → None
Requests emission of the
MenuModel::items-changed signal onmodel.This function should never be called except by
MenuModelsubclasses. Any other calls to this function will very likely lead to a violation of the interface of the model.The implementation should update its internal representation of the menu before emitting the signal. The implementation should further expect to receive queries about the new state of the menu (and particularly added menu items) while signal handlers are running.
The implementation must dispatch this call directly from a mainloop entry and not in response to calls – particularly those from the
MenuModelAPI. Said another way: the menu must not change while user code is running without returning to the mainloop.Added in version 2.32.
- Parameters:
position – the position of the change
removed – the number of items removed
added – the number of items added
- iterate_item_attributes(item_index: int) → MenuAttributeIter
Creates a
MenuAttributeIterto iterate over the attributes of the item at positionitem_indexinmodel.You must free the iterator with
unref()when you are done.Added in version 2.32.
- Parameters:
item_index – the index of the item
- iterate_item_links(item_index: int) → MenuLinkIter
Creates a
MenuLinkIterto iterate over the links of the item at positionitem_indexinmodel.You must free the iterator with
unref()when you are done.Added in version 2.32.
- Parameters:
item_index – the index of the item
Signals
- class MenuModel.signals
- items_changed(position: int, removed: int, added: int) → None
Emitted when a change has occurred to the menu.
The only changes that can occur to a menu is that items are removed or added. Items may not change (except by being removed and added back in the same location). This signal is capable of describing both of those changes (at the same time).
The signal means that starting at the index
position,removeditems were removed andaddeditems were added in their place. Ifremovedis zero then only items were added. Ifaddedis zero then only items were removed.As an example, if the menu contains items a, b, c, d (in that order) and the signal (2, 1, 3) occurs then the new composition of the menu will be a, b, *, *, *, d (with each * representing some new item).
Signal handlers may query the model (particularly the added items) and expect to see the results of the modification that is being reported. The signal is emitted after the modification.
- Parameters:
position – the position of the change
removed – the number of items removed
added – the number of items added
Virtual Methods
- class MenuModel
- do_get_item_attribute_value(item_index: int, attribute: str, expected_type: VariantType | None = None) → Variant | None
Queries the item at position
item_indexinmodelfor the attribute specified byattribute.If
expected_typeis non-Nonethen it specifies the expected type of the attribute. If it isNonethen any type will be accepted.If the attribute exists and matches
expected_type(or if the expected type is unspecified) then the value is returned.If the attribute does not exist, or does not match the expected type then
Noneis returned.Added in version 2.32.
- Parameters:
item_index – the index of the item
attribute – the attribute to query
expected_type – the expected type of the attribute, or
None
- do_get_item_attributes(item_index: int) → dict[str, Variant]
Gets all the attributes associated with the item in the menu model.
- Parameters:
item_index – The
MenuItemto query
- do_get_item_link(item_index: int, link: str) → MenuModel | None
Queries the item at position
item_indexinmodelfor the link specified bylink.If the link exists, the linked
MenuModelis returned. If the link does not exist,Noneis returned.Added in version 2.32.
- Parameters:
item_index – the index of the item
link – the link to query
- do_get_item_links(item_index: int) → dict[str, MenuModel]
Gets all the links associated with the item in the menu model.
- Parameters:
item_index – The
MenuItemto query
- do_is_mutable() → bool
Queries if
modelis mutable.An immutable
MenuModelwill never emit theMenuModel::items-changed signal. Consumers of the model may make optimisations accordingly.Added in version 2.32.
- do_iterate_item_attributes(item_index: int) → MenuAttributeIter
Creates a
MenuAttributeIterto iterate over the attributes of the item at positionitem_indexinmodel.You must free the iterator with
unref()when you are done.Added in version 2.32.
- Parameters:
item_index – the index of the item
- do_iterate_item_links(item_index: int) → MenuLinkIter
Creates a
MenuLinkIterto iterate over the links of the item at positionitem_indexinmodel.You must free the iterator with
unref()when you are done.Added in version 2.32.
- Parameters:
item_index – the index of the item